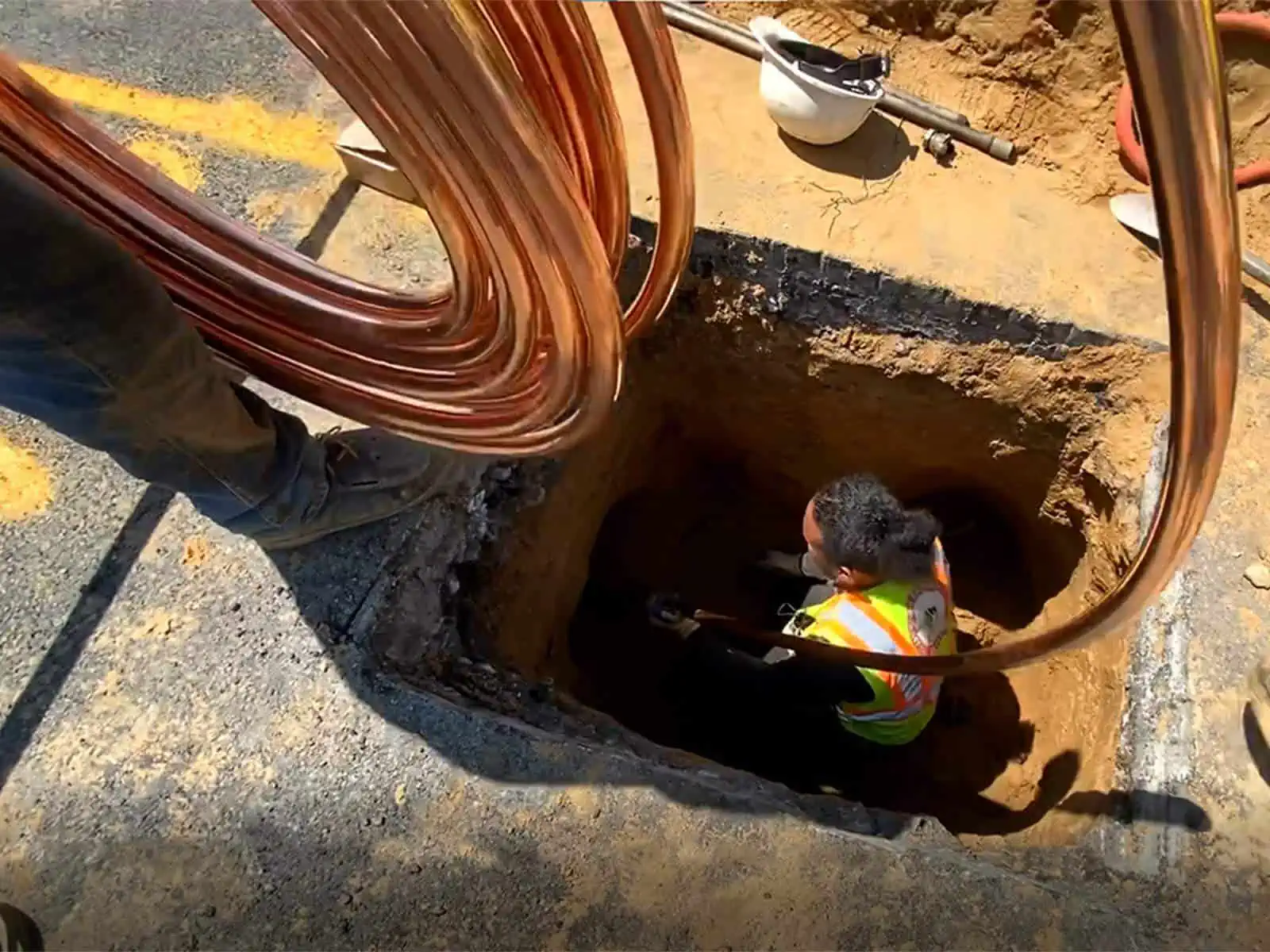
In New York City, copper, brass, and ductile iron pipes are commonly used for potable water systems. Lead, galvanized, PVC, and PEX piping are not among the 3 approved types of pipes allowed for water lines by the New York City code for water lines. However, galvanized and lead water lines are still present inside some buildings. In those cases, they are “grandfathered in” and allowed to remain in place, but not replaced in kind with lead or galvanized pipe.

The 3 Types of Water Line Pipe Allowed to Be Installed In NYC
Knowing the following information may only seem to be meaningful to NYC plumbers, but it can help homeowners avoid code violations and protect their drinking water from impurities. Every type of material seemingly has its unique pipes pros and cons, but not all are legal for use in every circumstance.
1. K Copper and L Copper Water Pipes:
Both K copper and L copper are the most widely used types of line water pipe due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for both hot and cold water. They also meet NYC plumbing code requirements.
K copper water tubing is used for underground water service lines, primarily due to its malleability. This gives K copper the ability to bend and move along with ground shifts or ground settlements without leaking. K copper water tubing is connected by flaring each end of the copper, then using special fittings to form the leak-free connections. On the other hand, L copper is rigid, and primarily used for indoor house water piping.
2. Brass Water Pipes:
Brass pipes, typically made from an alloy of copper and zinc, are durable and resistant to corrosion. Brass is commonly used for water service lines, house plumbing, water distribution systems, and as fittings for all sorts of plumbing applications. While included in the types of water line pipe that are approved, brass is not frequently used for water service lines due to its relatively high cost.
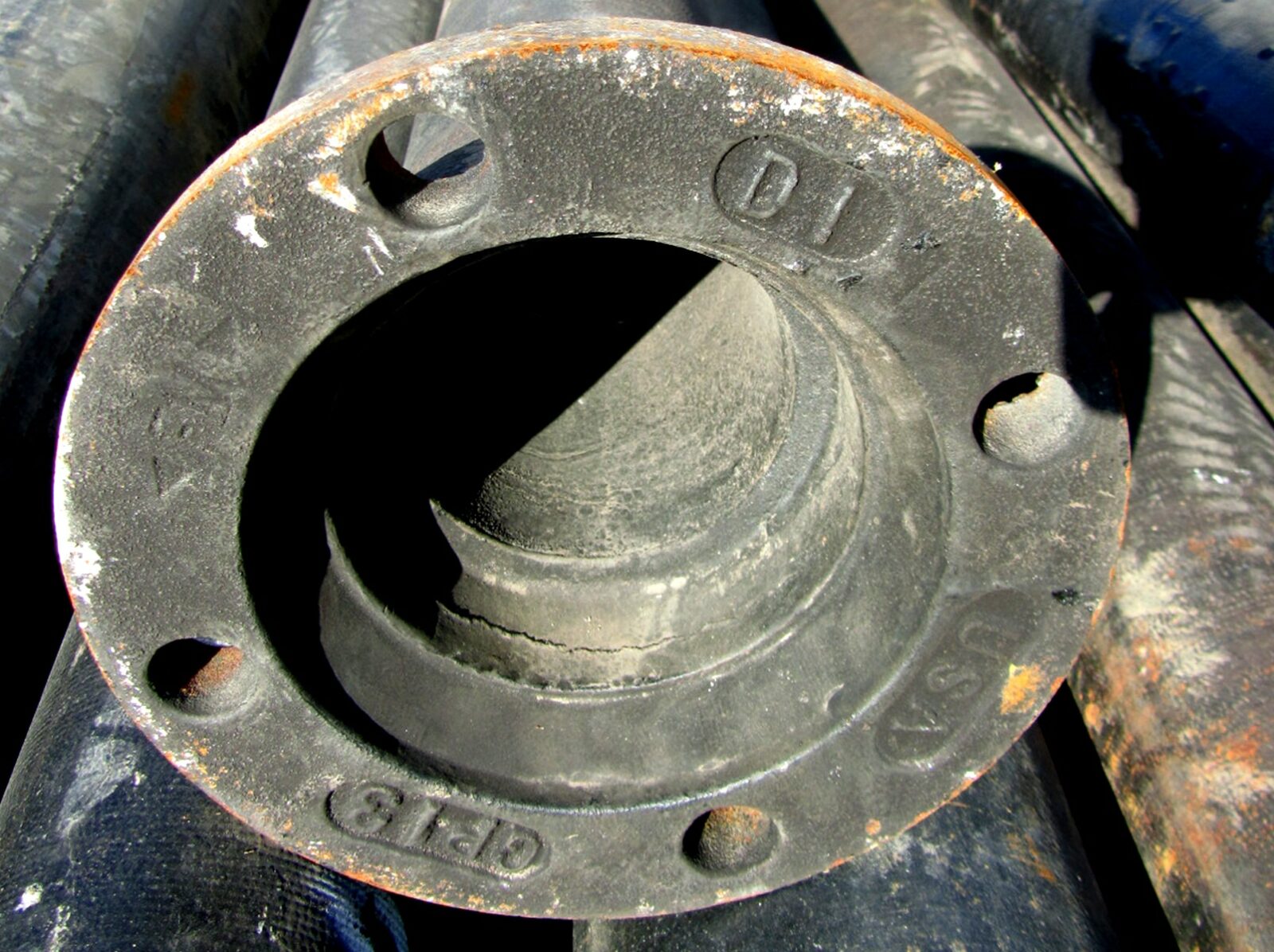
3. Ductile Iron Water Pipes:
Ductile iron pipes are a type of cast iron pipes that are known for their strength and durability. These characteristics make ductule iron suitable for both underground water service lines and larger water public water supply lines as well.
There are various types of ductile iron pipes, and they can be used for different purposes. In the case of ductile iron water pipe, it is cement-lined and joined together using gaskets and retainer glands.

Galvanized Steel Pipes and Lead Water Lines in Older Buildings:
While rarely if ever found in newer construction due to concerns about galvanized pipe corrosion and code compliance, some older buildings might still have galvanized pipes or lead water lines.
When a replacement of a lead or galvanized water line is needed, newer and code-compliant materials such as copper, brass, or ductile iron are recommended and must be used to typically meet the local plumbing code.
How are Different Types of Water Line Pipe Made?
The 5 Step Copper Water Tubing Manufacturing Process
Regardless of the grade, size, and type of water line pipe that is copper, they are of universally high quality, and copper water lines are long-lasting. With that having been said, the 5 step manufacturing process of copper may be of some interest.
- The Extraction and Refinement Process: Copper is first mined from ore deposits, and then refined through various processes to achieve the high purity levels required for plumbing applications.
- Forming Billets or Ingots of Refined Copper: The refined copper is melted and cast into billets or ingots, which are cylindrical shapes, then suitable for the next step in the process.
- Extrusion or Drawing of the Melted Copper: The copper billets are heated and then passed through a series of dies which form long, continuous tubes of copper. This part of the copper water pipe process might involve extrusion (which is forcing metal through a shaped opening) or drawing the copper (pulling the copper through a series of progressively smaller and smaller dies). Either of these methods achieves the desired diameter and thickness of the copper water tubing.
- Annealing the Copper Water Tubing: After shaping the copper, the tubing is annealed by heating it to about 700 degrees Fahrenheit and slowly cooling it to relieve internal stresses and improve its malleability. The annealing process is key to making copper easier to bend and shape during the installation process.
- Finishing the Copper is The Final Step: The copper water tubing is cut to specific lengths. L copper is typically shipped from the manufacturer at 20′ lengths. While K copper is shipped in coils that can range from 40′ to 100′. Before it is shipped, it is cleaned to remove any residue and may also undergo some surface treatments or coatings to enhance corrosion resistance or prevent the growth of bacteria.
The 4 Step Ductile Iron Pipe Manufacturing Process
Ductile iron pipe was invented around 1943 and is used for different applications. It is likewise manufactured and coated in different ways depending on its intended use. When ductile iron pipe is being made for water supply lines, it has a cement lining. It is extremely strong, and able to withstand ground settlement and shifting. Ductile Iron pipe is considered a far more durable pipe than cast iron, which used to be used for municipal water supply lines.
- The Melting and Casting Process for Ductile Iron Pipe: Iron ore is melted at around 2100 degrees Fahrenheit in a furnace along with scrap iron and other alloying elements like carbon, silicon, and magnesium within very specific tolerances. This molten metal mixture is then poured into molds to create pipe sections.
- The Centrifugal Casting or Molding Process: The most common method for making any type of ductile iron pipes involves centrifugal casting. In this process, the molten metal is spun rapidly inside a mold. Using a centrifugal casting process allows for an even distribution of the molten material against the mold’s inner surface, forming the pipe.
- Annealing and Heat Treatment: These newly formed pipes are then subjected to a controlled heat treatment process, which enhances their ductility, strength, and resistance to fractures.
- Machining and Finishing the Ductile Iron Pipe: After cooling the newly formed pipes, they undergo various machining processes. Both the machining and finishing processes of the ductule iron pipe ensure uniformity in each pipe’s diameter, smoothness, and the removal of any pipe imperfections. Ductile iron pipes also frequently receive protective coatings or linings to prevent corrosion, depending on their intended end use.
Both copper water tubing and ductile iron pipes are manufactured to meet very specific standards. This ensures that they possess the necessary qualities of durability, strength, and corrosion resistance required for their respective plumbing end-use and that they are code-compliant.
The Importance of Knowing the Types of Water Line Pipe Allowed by Your Local Plumbing Code
Before a plumber undertakes any plumbing work or selects materials for potable (drinking) water systems in New York City, it’s crucial to check and adhere to the most current Department of Buildings Plumbing Code, as is true regardless of the locale and applicable plumbing code. These codes will specify permitted types of water line pipe materials, installation methods, and other requirements to ensure the safety and compliance of the water that is supplied to your premises.
Regardless of if a water line repair or a full replacement is being done, approved materials must be used. And to reiterate, repairs on existing lead or galvanized water service lines is not permitted by code in NYC.
Local Plumbing Codes Vary by Jurisdiction
Local plumbing codes can vary and might have specific guidelines or restrictions that homeowners and plumbers need to follow. Of note, is that if a material is not listed in the code it is not permitted. It’s advisable to consult and use a Licensed Master Plumber in New York City, or wherever you reside when it involves your drinking water supply.
Team Balkan – The Team You Trust
If you reside in the New York City area and require water service line work, Balkan Sewer And Water Main Service is the largest and most trusted service. Team Balkan has been in continuous operation for over 70 years, with a proud family history, and has a client list that exceeds 90,000 happy New Yorkers.