A standpipe connection can be a lifesaver in case of a fire. Firefighters rely on standpipe connections to save lives and minimize property damage. The end result is that standpipes are an excellent innovation. They enable firefighters to suppress fires even when they break out on high-rise buildings.
The Committee on Standpipe and Hose Systems first codified standpipes in 1914. This innovation came about when skyscrapers were beginning to dominate the construction industry. Skyscrapers and hi-rise buildings created a safety challenge for firefighters. Firefighters now needed solutions for combating fires on upper floors.
In 1915, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) adopted the standpipe code. It remains the basis of the current NFPA 14. NFPA 14 contains the Standards for the Installation of Standpipes and Hose Systems. But you probably do not know what a standpipe system is. Let’s define it for you.
What is a Standpipe System?
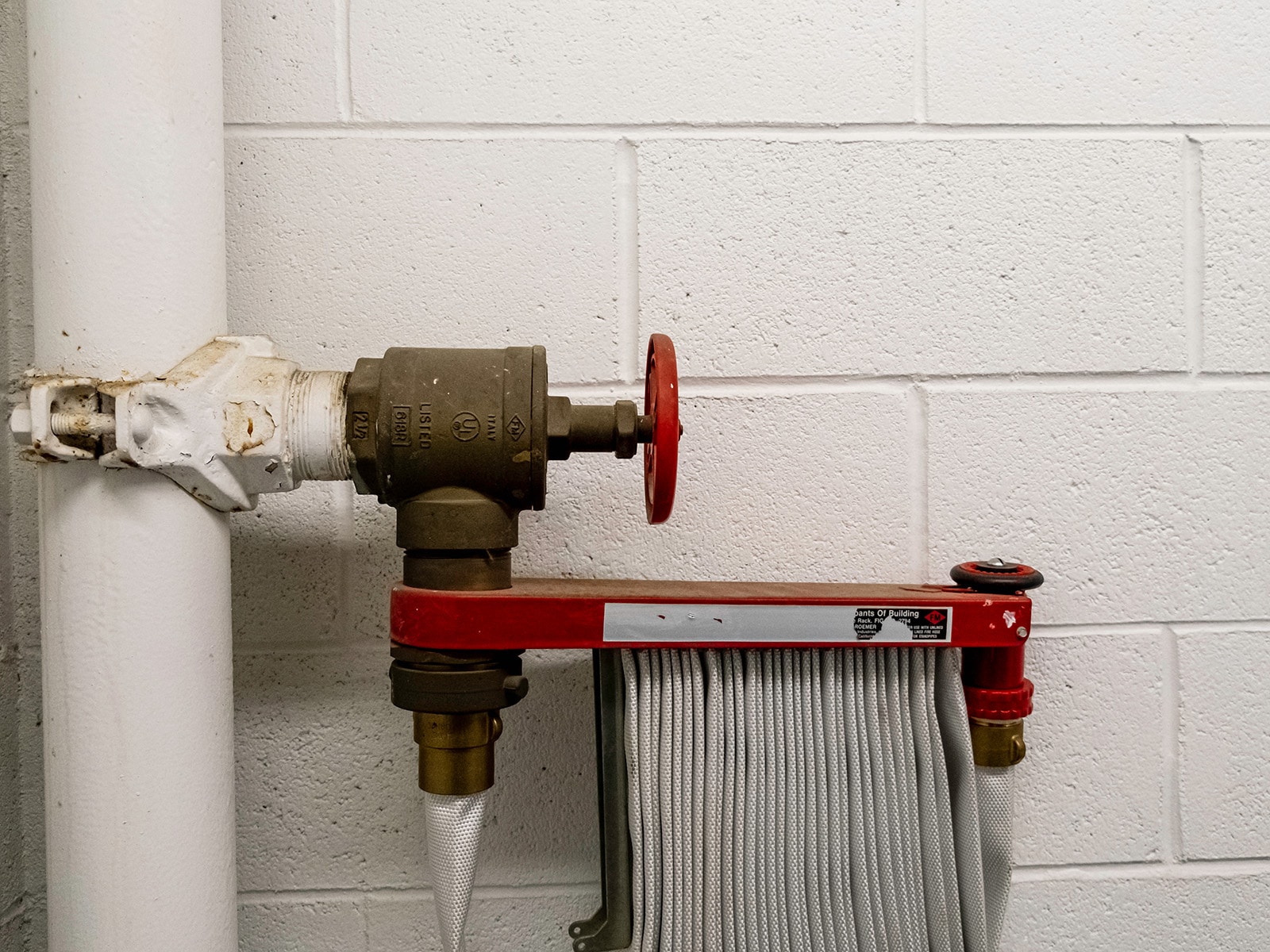
Inside the structure of a building a standpipe is a collection of piping, hose connections, valves, as well as accompanying equipment. Their sole purpose is to help extinguish a fire to protect lives and property. The positioning of the hose connection allows water to be discharged in spray patterns or streams once the hoses as well as nozzles are connected.
The standpipe system also has numerous outlets located on each floor of a building. This enables firefighters to reach all the areas in a building. However, they are designed differently to accommodate various fire safety needs of property owners and firefighters. Read on to learn about the different classes of standpipes systems.
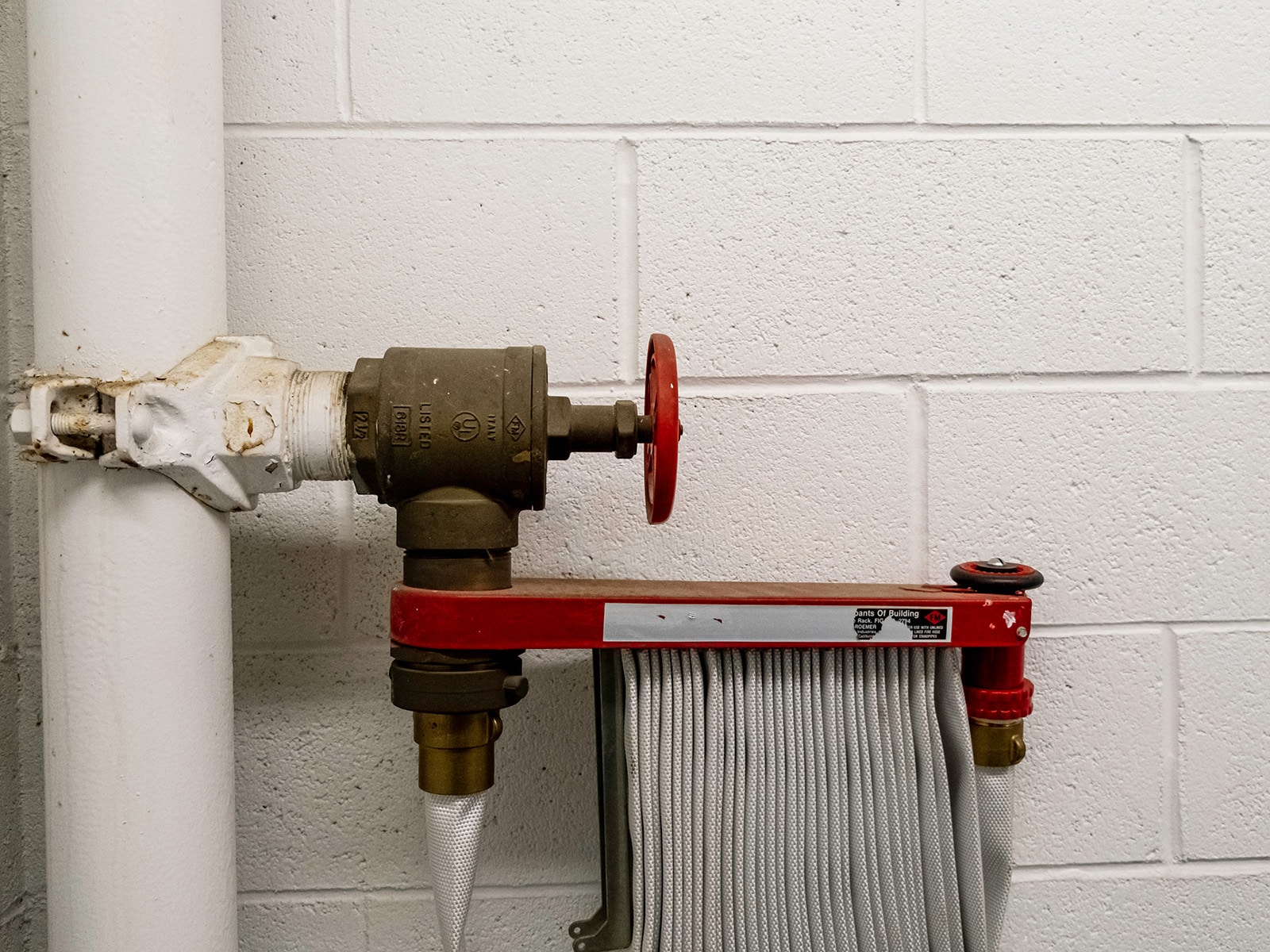

Classes of Standpipes Systems
Class I Standpipe Systems
These systems are restricted for use by professional firefighters as they release water under high pressure that may be hard for an inexperienced person to control. Their outlets are usually installed within building stairwells.
Firefighters usually carry a unique hose to attach to class I standpipe connections. In most places, you can fit a 2.5″ hose. However, in New York and San Francisco, you can fit a 3″ hose to your class 1 standpipe.
Class II Standpipe Systems
They are common on hallways of buildings, mostly accommodating a 1.5″ hose. They are easy to operate and can be accessed and used by anybody. However, property owners are increasingly shunning them. There has been a heightened safety risk of inexperienced people trying to use them to put out fires and getting hurt in the process. As a result, they mostly exist on old buildings, with new building owners preferring domestic fire sprinklers.
Class III Standpipe Systems
This is a hybrid of class I and Class II standpipe systems. They have permanently fixed 1.5″ hoses for use by inexperienced firefighters. And 2.5″ hose connections where professional firefighters attach their hoses. Some Class III systems have 2.5″ connections and reducers with 1.5″ hoses permanently attached. But some do not include the permanent 1.5″ hose.

How are Standpipes Fed Water?
Standpipes are essential for delivering water in an emergency. You can install a standpipe and fill it with water or leave it dry. However, you must carry out a pre-incident assessment to ensure your components, including the water pump, are in place and working. Here are the types of standpipes you can use when fighting a fire.
Wet System
It has constant water and consistent water pressure. This system is permanently fixed to a reliable water supply with a manual regulating valve.
Manual Dry Systems
The pipes in this system contain no water or air. Firefighters use a fire apparatus to feed them with water.
Automatic Dry Standpipes
They are filled with water to maintain constant pressure. You release the air in the system when you connect the hose in an emergency and replace it with water.
Semi-Automatic Dry Standpipe
This system stores pressurized or unpressurized air in the pipes. When you activate the manual pull station or electrical switch, water flows in as the air escapes from the far end.
Maintaining and Testing Standpipe Systems
After installing your standpipe, you want to test it to ensure it can deliver water effectively in an emergency. Testing is also done after a major modification of a structure.Testing is also essential during the demolition of a building. This initial testing done on the new or modified building is referred to as acceptance testing. Let’s explore the two testing requirements here:
Acceptance Testing
Standpipe acceptance testing is done sequentially, beginning with the underground components and proceeding to the subsequent levels. Testing underground standpipe components helps the contractor identify faults like blockage or leakages. It also helps them repair the underground parts to avoid compromising the effectiveness of the system components on higher levels.
During underground testing, debris is flushed from the system to avoid blockage. A hydrostatic test then follows to ensure there are no breakages, leakages, as well as pressure loss. The hydrostatic test should run for about 2 hours as you pump water from the lowest point and monitor the pressure.
NPFA 25 regulations allow a pressure loss of up to 5psi as you may not tighten joints to avoid small leaks. If the pressure drops beyond that, there could be another problem.
Above-Ground Testing
You can do your above-ground testing immediately after the underground test. Here, you also begin by flushing debris from the components. Follow this with a hydrostatic test for leaks and pressure loss.
This involves capping all the outlets and running pressurized water through the standpipe system for about 2 hours. For best results, pump water from the lowest point in every zone and monitor the gauge consistently for any pressure drop.
Above-ground hydrostatic testing doesn’t allow pressure loss. Unlike in underground testing where a small margin of pressure loss is acceptable. Test the connections to ensure they are compatible with your local authority hose type specifications.
You should also test if the system delivers water to the furthest point of the structure. Class I and III require a 100psi pressure at the most remote point, while class II systems require a 65psi to the same point.
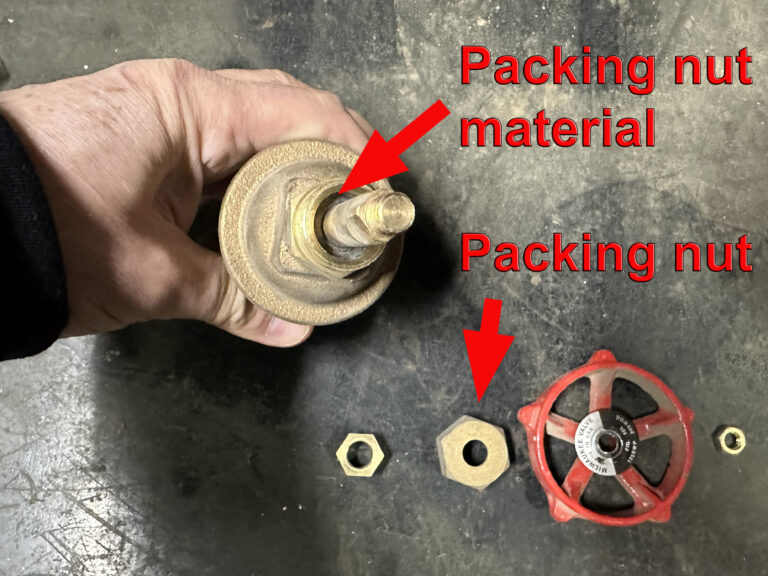
Test if the pressure reducing parts work as intended and that the valves are open. Use the initial test as your benchmark for pressure reading you will use in maintenance testing. The process for maintenance testing will be similar, identifying and replacing faulty components.
How We Can Help
Are you looking for a plumbing company to install a new fire service main, or upgrade an existing fire main? Reach out to Balkan Sewer and Water Main. Having a professionally installed fire service main is perhaps the vital component to ensure a properly functioning standpipe connection.
We are the largest and most trusted sewer and water Main Service company in New York City, with a record of about 80,000 completed projects. Contact us to discuss your water and sewer project.